-
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
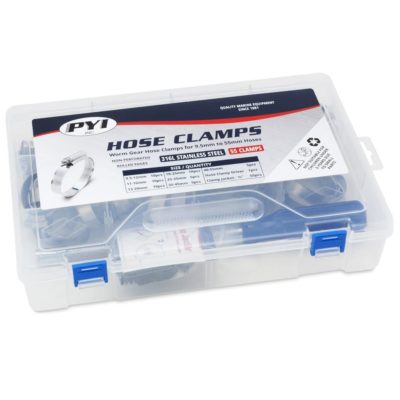
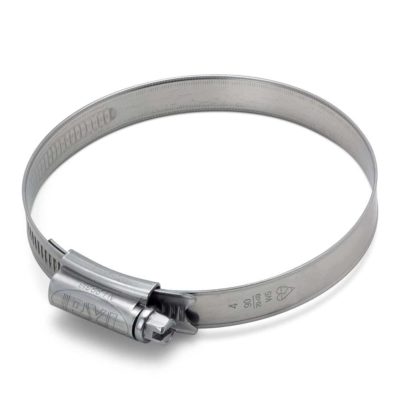
Worm Gear Hose Clamp

-
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
CLAMP JACKET : Hose Clamp Tail Covers


PYI Worm Gear Hose Clamp

Safe For All Types of Hoses
By rolling the edges and removing perforations and ribs on the inside portion of the embossed hose band, the PYI Hose Clamp can be used on the softest hoses without worry of damage to the underlying hose surface during installation and throughout its use.
Durable & Stable Clamping Force
The PYI Hose Clamp utilizes a durable double locked screw cage design that is machined from a single piece of 316L stainless steel which is capable of withstanding high tightening torque and internal hose pressure. Our Hose Clamps can be hand tightened up to 15.5 NM (135 in/lbs.) without the screw slipping or distorting the screw cage during its installation and use providing a reliably strong and stable clamping force and a long-lasting hold that is ideal for most demanding applications.
Reliable
PYI Hose Clamps are manufactured entirely out of 316L Stainless Steel giving them excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals and acids that could limit the life of other metals. Whether used industrially or around the house, the PYI Hose Clamp will keep your hose secure in some of the harshest environments.
Quality at Every Level of Manufacturing
Tested and certified under ISO 9001:2015, these standards assure the excellent design and manufacturing quality across the entire manufacturing process, from inception to implementation.
316L Stainless Steel

316L stainless steel utilizes a higher percentage of molybdenum, chromium and nickel than 304 stainless steel. The addition of these elements, notably molybdenum, improves the resistance to corrosion and chloride pitting, provides a greater creep resistance, and a stronger stress-to-rupture and tensile strength at elevated temperatures.
- 316L has slightly less Carbon in it then 316 making it a better choice for welding.
- 316L a great stainless steel for high-temperature, high-corrosion uses, which is why it's so popular for use in construction and marine projects.
- The lower carbon content in 316L minimizes deleterious carbide precipitation as a result of welding. Consequently, 316L is used when welding is required in order to ensure maximum corrosion resistance.
316 is the standard marine grade stainless steel due to its excellent resistance to corrosion in harsh environments. 316L SS utilizes a higher percentage of molybdenum, chromium and nickel than other grades of Stainless Steel, while also having a very small amount of Carbon as compared to other grades of Stainless Steel. The addition of these elements, notably molybdenum, improves the stainless steel’s strength, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand harsh chemicals and acids.
Benefits to Adding Molybdenum:
Most commercial molybdenum is used in the production of alloys, where it is added to increase hardness, strength, electrical conductivity and resistance to wear and corrosion.
- Molybdenum improves Stainless Steel’s general resistance to corrosion and chloride pitting which helps to lengthen the usable life of Stainless Steel and allows the PYI Hose Clamp to maintain a strong clamping force throughout its useful life.
- Molybdenum provides a greater creep (cold flow) resistance over time. Creep, in the material sciences, is a material’s ability to change its shape or slowly deform permanently over time. This allows the PYI Hose Clamps to provide a consistent clamping force throughout its useful life without damage or disfigurement due to constant tension on the hose clamp during use.
- The addition of molybdenum gives the Stainless Steel a stronger stress-to-rupture and ultimate tensile strength at elevated temperatures, up to 932°F (500°C). Stress-to-rupture is a sudden and complete failure of a material under stress load. Ultimate tensile strength is a material’s ability to withstand tension which tries to pull the material apart, as opposed to compress the material.
316L Stainless Steel
PYI Hose Clamps are manufactured in a facility that is ISO 9001:2015 certified by Bureau Veritas.
- Passed a Salt Spray Test >1000 Hours for red rust formation
- Report Test No: 8505062
- Test No: 8590868
- Issue Date: July 27, 2016
specifications
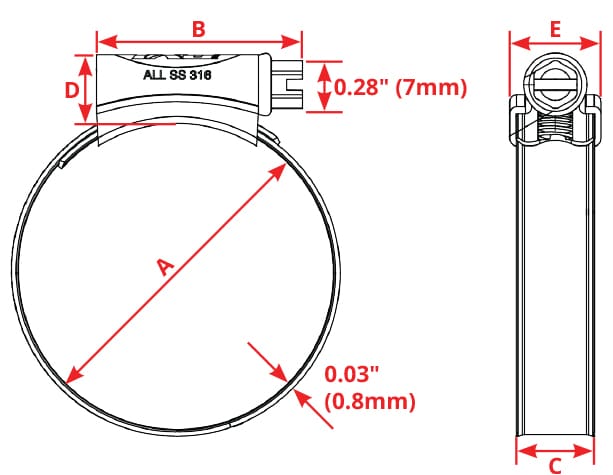
| Part # | SAE | A | B | C | D | E | Recommended Torque | Max Operating Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 07-HC1-2 | - | 0.37" - 0.47" (9.5mm - 12mm) | 0.75" (19mm) | 0.37" (9mm) | 0.39" (10mm) | 0.48" (12.3mm) | 3.4 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-6 | 4 | 0.43" - 0.63" (11mm - 16mm) | 0.75" (19mm) | 0.37" (9.5mm) | 0.39" (10mm) | 0.48" (12.3mm) | 3.4 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC2-0 | 8 | 0.50" - 0.79" (13mm - 20mm) | 0.75" (19mm) | 0.37" (9.5mm) | 0.39" (10mm) | 0.48" (12.3mm) | 3.4 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC2-2 | 8 | 0.63" - 0.87" (16mm - 22mm) | 0.94" (24.0mm) | 0.47" (12.0mm) | 0.50" (12.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 4.2 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC2-5 | 10 | 0.71" - 0.98" (18mm - 25mm) | 0.94" (24.0mm) | 0.47" (12.0mm) | 0.50" (12.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 4.2 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC3-0 | 12 | 0.87" - 1.18" (22mm - 30mm) | 0.94" (24mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.1 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC3-5 | 16 | 0.98" - 1.38" (25mm - 35mm) | 0.94" (24mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.1 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC4-0 | 20 | 1.18" - 1.57" (30mm - 40mm) | 0.94" (24mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.1 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC4-5 | 20, 22 | 1.38" - 1.78" (35mm - 45mm) | 0.94" (24mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.1 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC5-0 | 24 | 1.38" - 1.97" (35mm - 45mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC5-5 | 24, 28 | 1.57" - 2.16" (40mm - 55mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC6-0 | 28, 32 | 1.78" - 2.36" (45mm - 60mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC7-0 | 34, 36 | 2.17" - 2.76" (55mm - 70mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC8-0 | 40, 44 | 2.36" - 3.15" (60mm - 80mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 6.8 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC9-0 | 48 | 2.76" - 3.54" (70mm - 90mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 6.8 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-00 | 52, 56 | 3.35" - 3.94" (85mm - 100mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.50" (12.5mm) | 0.58"(14.65mm) | 6.8 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-20 | 60, 64 | 3.54" - 4.72" (90mm - 120mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.50" (12.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 6.8 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-25 | 64, 80 | 3.94" - 4.92" (100mm - 125mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.50" (12.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 6.8 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-40 | 72, 80 | 4.72" - 5.51" (120mm - 140mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 6.8 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-50 | 88 | 5.11" - 5.91" (130mm - 150mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 6.8 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-60 | 96 | 5.12" - 6.30" (130mm - 160mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC1-80 | 104 | 5.91" - 7.10" (150mm - 180mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC2-00 | 104, 122 | 6.70" - 7.87" (170mm - 200mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC2-30 | 122, 138 | 7.48" - 9.05" (190mm - 230mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC2-50 | 138, 154 | 8.66" - 9.84" (220mm - 250mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC2-80 | 154, 170 | 9.45" - 11.02" (240mm - 280mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC3-00 | 170, 186 | 10.63" - 11.80" (270mm - 300mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC3-30 | 200 | 11.42" - 13" (290mm - 330mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC3-60 | 224 | 12.60" - 14.17" (320mm - 360mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
| 07-HC3-80 | 224 | 13.78" - 14.96" (350mm - 380mm) | 1.30" (33mm) | 0.47" (12mm) | 0.45" (11.5mm) | 0.58" (14.65mm) | 5.9 N.m | 500°C (932°F) |
testing
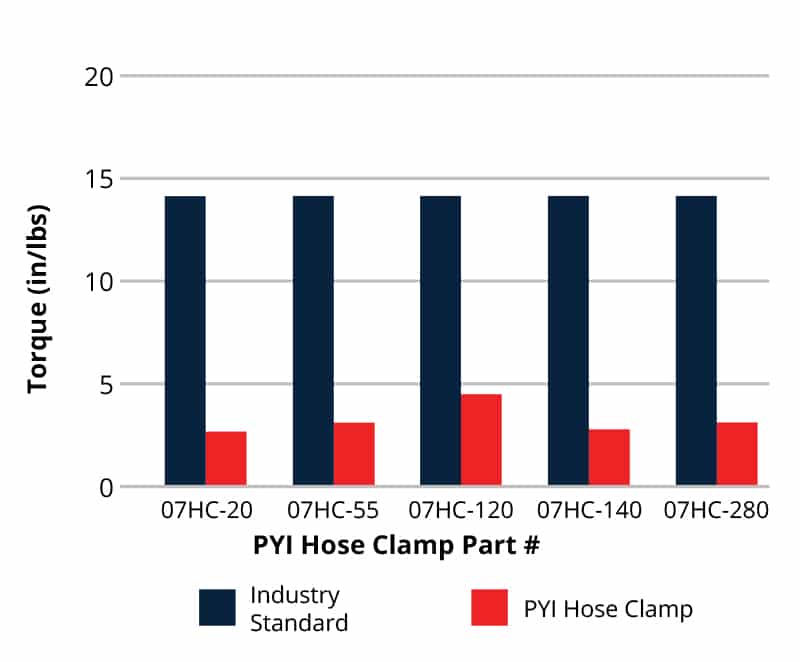
Lower Idle Torque Test
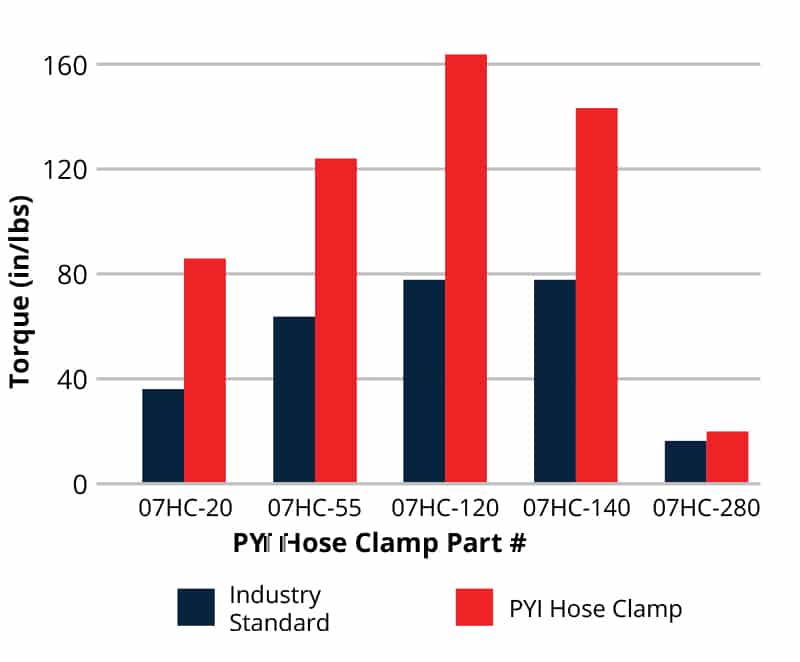
Destructive Turning Torque Test
Applications

Automotive

Lawn Mower / Tractor

Marine